62 The Cell Cycle Concepts of Biology 1st Canadian Edition Biology Diagrams The cell cycle consists of distinct phases that guide cellular activities from one stage to the next. Each phase has specific functions and checkpoints to maintain genomic integrity and prevent errors. G1 Phase (Cell Growth) The G1 phase, often referred to as the first gap phase, is a period of cellular growth and metabolic activity. M phase is the most dramatic period of the cell cycle, involving a major reorganization of virtually all cell components. During mitosis (nuclear division), the chromosomes condense, the nuclear envelope of most cells breaks down, the cytoskeleton reorganizes to form the mitotic spindle, and the chromosomes move to opposite poles. Chromosome segregation is then usually followed by cell
In most animal cells, M phase takes only about an hour—a small fraction of the total cell-cycle time, which often lasts 12-24 hours. The rest of the cycle is occupied by interphase . Under the microscope, interphase appears as a deceptively uneventful interlude, in which the cell simply continues to grow in size.
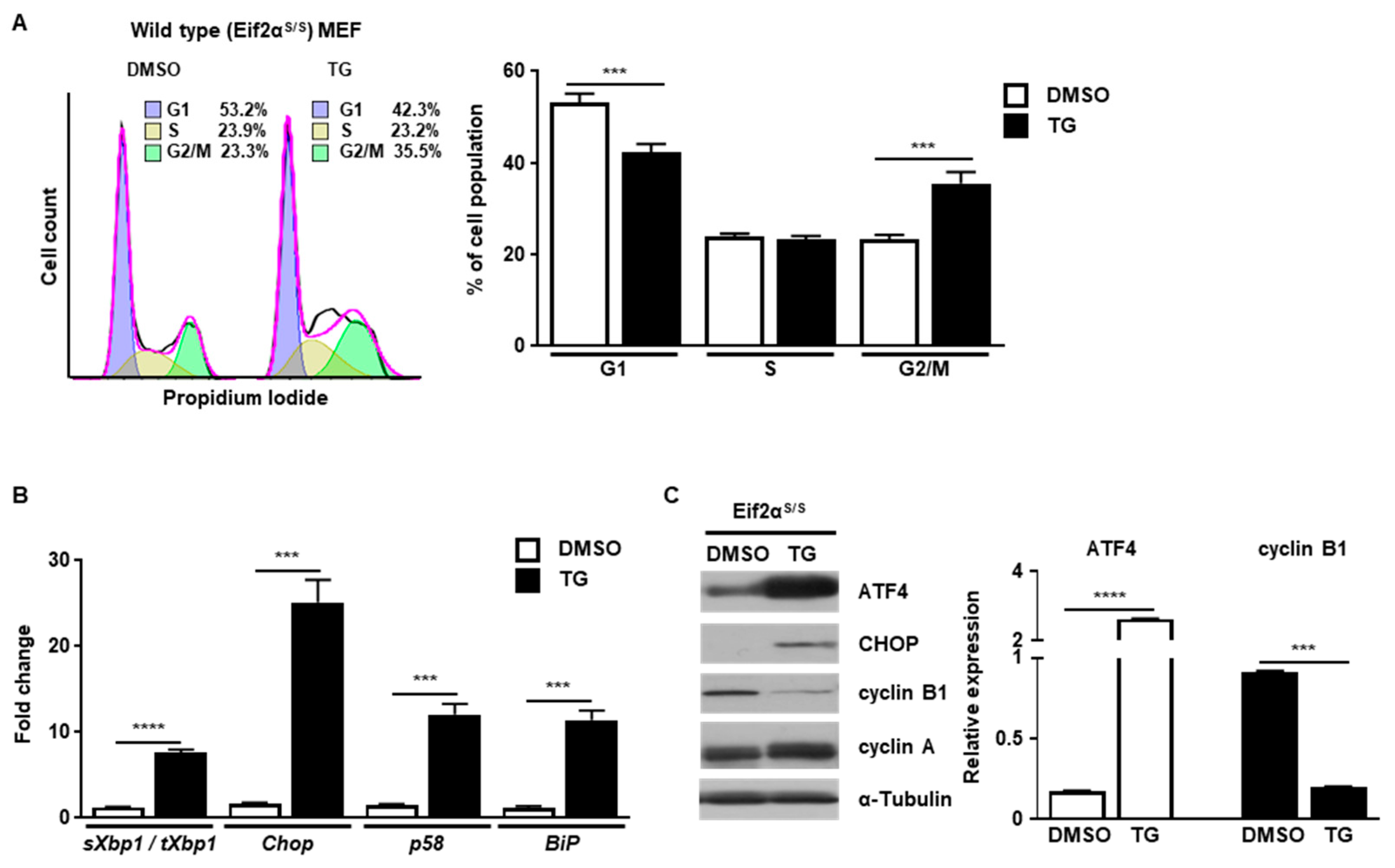
Molecular Biology of the Cell Biology Diagrams
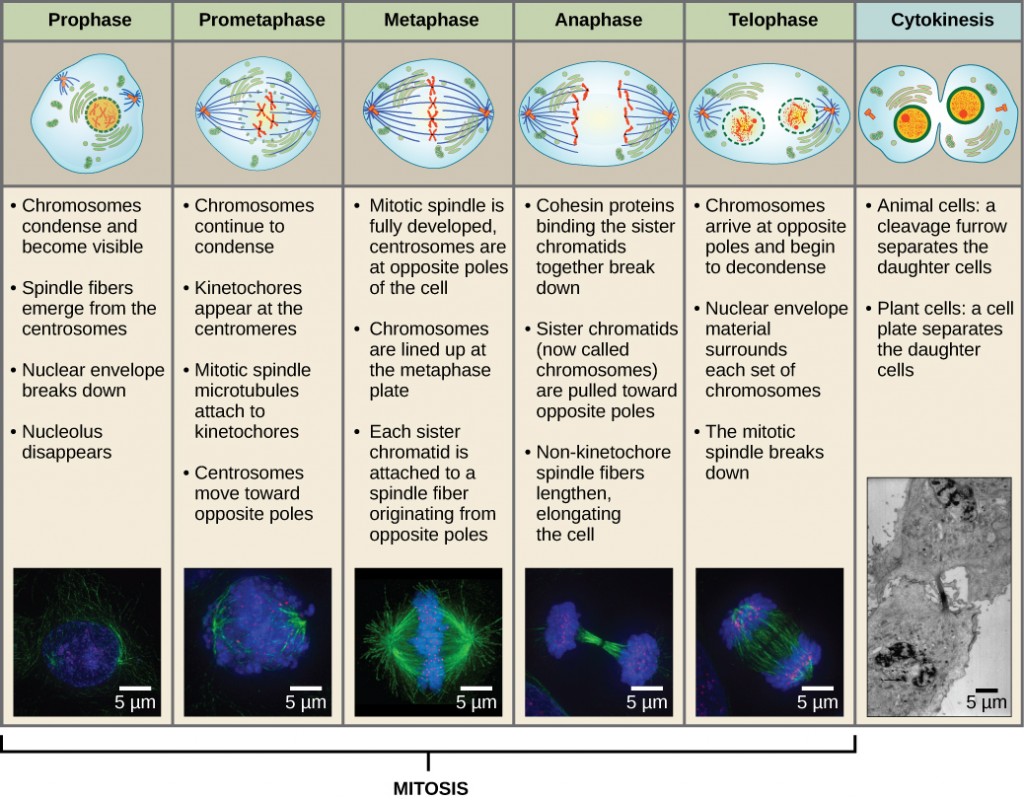
The M phase of a cell cycle is also called mitosis. This is a form of asexual cell reproduction in eukaryotes, equivalent in most respects to binary fission in prokaryotes. In includes prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase, and it relies on the mitotic spindle at each cell pole. The M-Phase, also known as the Mitotic Phase, is a stage in the cell cycle where cell division occurs. It is divided into several stages: Prophase: In this stage, the chromatin condenses into a highly ordered structure called chromosomes. The nuclear envelope breaks down and spindles start to form. Prometaphase: The nuclear envelope is completely broken down, and the chromosomes are free in
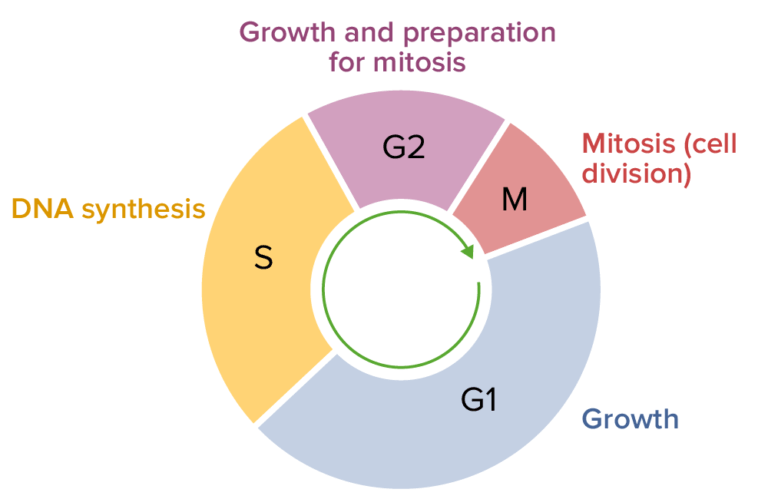
The cell cycle consists of a timed sequence of events that occur during interphase and mitosis (M). Interphase is made up of the G 1 (G = gap) phase, the S (synthesis) phase, and the G 2 phase (Fig. 15-2).Both G phases contain checkpoints that govern whether the cell moves into DNA replication (G 1 checkpoint) or into mitosis (G 2 checkpoint).. The G 1 and G 2 phases involve the synthesis of Overview of the Cell Cycle Phases. The two broad phases of the cell cycle are interphase and mitosis. During interphase, cells grow, replicate their DNA and organelles, and prepare for division. Interphase steps are the first gap phase (G 1), the synthesis phase (S), and the second gap phase (G 2). Cells divide during mitosis (M). It is the first phase of the cell cycle, recognized by the growth period where the chromosome gets duplicated as the cell prepares for division. Interphase happens between one cell division or mitotic (M) phase and the next. It is the longest part of the cell cycle involving three sub-phases. The typical duration of this phase is 23 hours.

Cell Cycle Phases and Checkpoints Biology Diagrams
The eukaryotic cell cycle consists of four distinct phases: G 1 phase, S phase (synthesis), G 2 phase (collectively known as interphase) and M phase (mitosis and cytokinesis). M phase is itself composed of two tightly coupled processes: mitosis, in which the cell's nucleus divides, and cytokinesis, in which the cell's cytoplasm and cell membrane divides forming two daughter cells.

