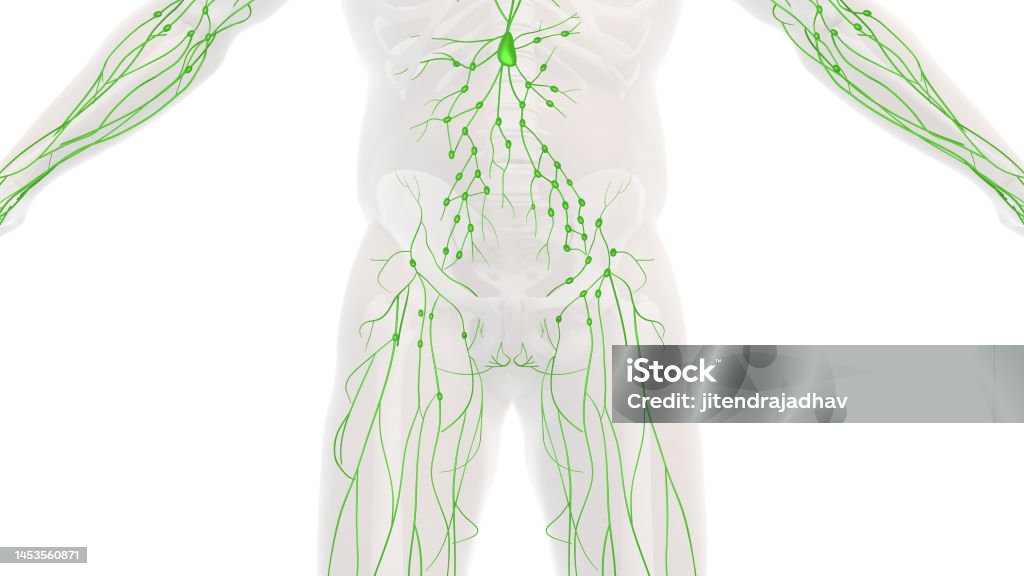
Anatomy Lymphatic System Humans 3d Illustration Stock Illustration Biology Diagrams The development of the lymphatic system is known from both human and animal, especially mouse studies. The lymphatic vessels form after the development of blood vessels, around six weeks post-fertilization. Lymphatic System. Illustrated anatomy includes the cervical lymph nodes, lymphatics of the mammary gland, cisterna chyli, lumbar lymph

Thymus. The thymus gland is a bilobed organ found in the space between the sternum and the aorta of the heart (Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)) that serves as a specialized structure in which T lymphocytes mature.The thymus is most active early in life as you are exposed to and build immunity to many pathogens. After puberty, the thymus slowly but continuously decreases in activity and size as its

Anatomy, Lymphatic System Biology Diagrams
The Lymphatic and Immune System Anatomy Human Lymphatic System. Introduction. The lymphatic system was first described in the 17th century independently by Olaus Rudbeck and Thomas Bartholin. The lymphatic system is an organ system closely associated with the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large
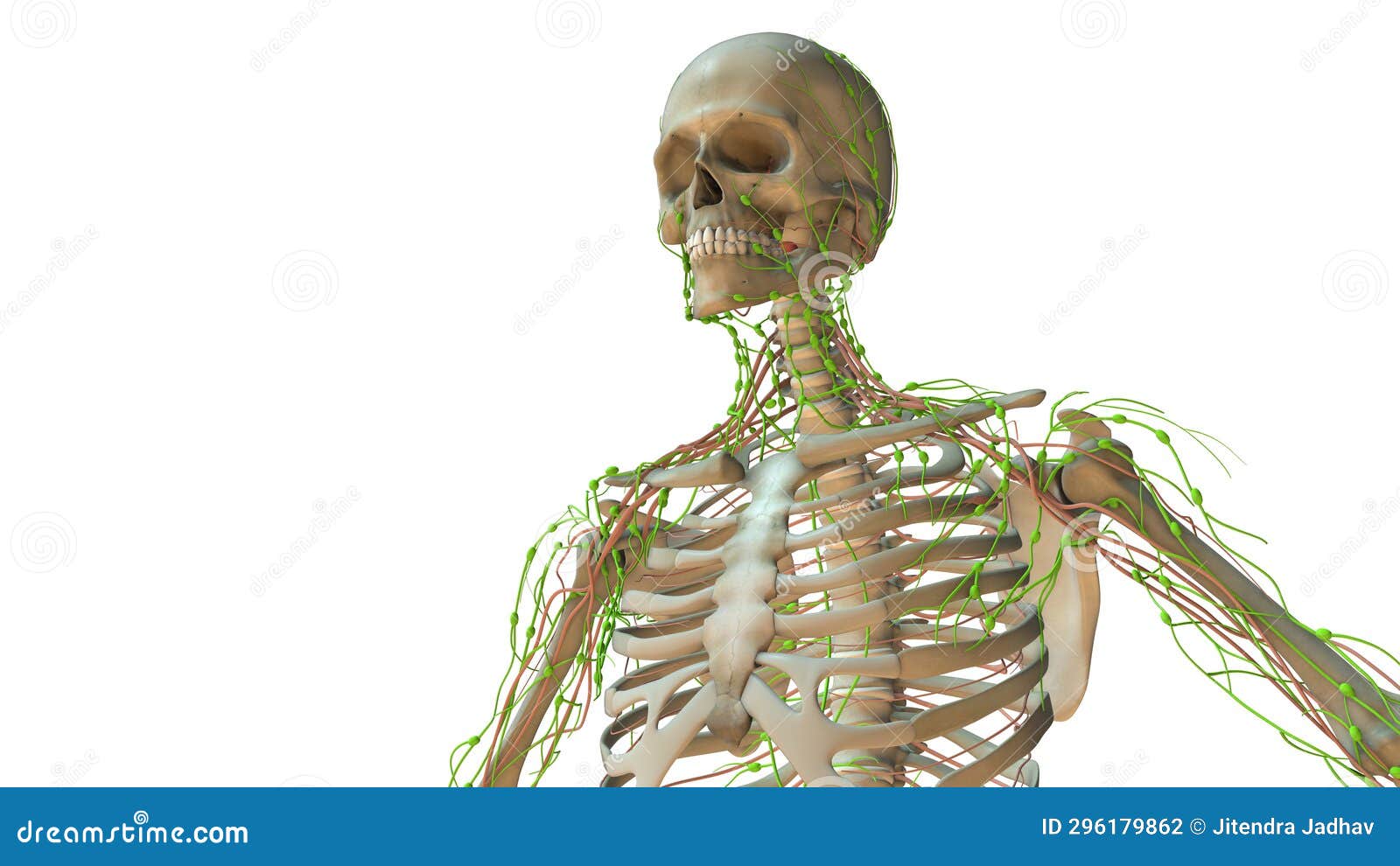
Anatomy of the Lymphatic System. The lymphatic system actually consists of two semi-independent parts: (1) a meandering network of lymphatic vessels and (2) various lymphoid tissues and organs scattered throughout the body. In passive immunity, the antibodies are obtained from the serum of an immune human or animal donor; as a result, the B
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1264199344-2fcaedbfb784455ca81d308e77ca6d40.jpg)
Lymphatic System: Function, Conditions & Disorders Biology Diagrams
Lymphatic tissue is a specialized form of reticular connective tissue that contains large numbers of lymphocytes The lymphatic system assists in circulating body fluids and helps defend the body against disease-causing agents. most components of blood plasma filter through blood capillary walls to form interstitial fluid. interstitial fluid passes into lymphatic vessels, it is called lymph The lymphatic system is commonly divided into the primary lymphoid organs, which are the sites of B and T cell maturation, and the secondary lymphoid organs, in which further differentiation of lymphocytes occurs.; Primary lymphoid organs include the thymus, bone marrow, and fetal liver and, in birds, a structure called the bursa of Fabricius.; In humans the thymus and bone marrow are the key

Anatomy. The lymphatic system begins with the lymphatic capillary meshwork that collects the excessive fluid from the tissues. The lymph travels from the tissues through larger lymph vessels until it reaches its destination point; the bloodstream. An adult human has an average of 450 lymph nodes, most of which are located in the abdomen. Human Body The Immune and Lymphatic Systems Learn all about the vessels, nodes, nodules, and ducts of the lymphatic system. Learn about lymph itself, bone marrow, and the different types of immunity. 3D models help you explore the anatomy and physiology. The lymphatic system also transports fatty acids from the intestines to the circulatory

19.4: Anatomy of Lymphatic Organs and Tissues Biology Diagrams
The lymphatic system is a network of organs, vessels and tissues that move a colorless fluid called lymph back to your bloodstream. Overview Function Anatomy Conditions and Disorders Care. Contents. When you see a diagram of the human body, your eyes might immediately go to the large organs like your heart or brain, or the red lines The lymphatic system is a crucial part of the circulatory and immune systems, often overlooked but vital for overall health. Composed of lymphatic vessels, nodes, and organs, this system serves multiple purposes, including immune defense, lipid absorption, and fluid balance.[7] Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th ed.). Hoboken, NJ: Pearson