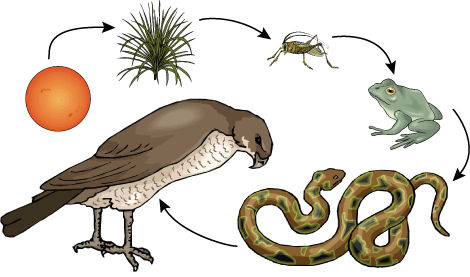
Evolution of Food Biology Diagrams The present article aims at understanding how species evolution and coevolution affects the response of a simple food chain subject to fertilization (bottom-up effect). The model without evolution is top-down controlled as in Oksanen et al.'s (1981) classical model. We show how evolution, or adaptive dynamics, affects the phenotypic traits at Allhoff et al. (2015) studied a version of a nonspatial food-web model of Loeuille and Loreau (2005) on two or eight discrete patches and investigated the effects of different dispersal patterns on emerged food webs, while Bolchoun et al. (2017) studied the effects of the topology of small networks of patches on food-web evolution. The earliest identified food chains seem to have concerned hyper-parasitism (Egerton 2005, 2006a), which students of insects discovered in the later 1600s.But it was entrepreneurial naturalist Richard Bradley (Egerton 2006b) who generalized the concept (Bradley 1718, part 3:60-61):Insects which prey upon others are not without some others of lesser Rank to feed upon them likewise, and so to

The current study supports an Eltonian view that our position in the food chain is conserved over long periods of evolutionary time. I suspect that both definitions are pertinent; habitat and our position on the food chain, our food network, are more interactive than the definitions suggest. In one notable example, David Post is focusing on how the alewife, a fish that lives in lakes in eastern North America, shapes and is shaped by its freshwater ecosystem. The community ecologist from Yale University and his colleagues have shown how these so-called eco-evo effects can ripple across a food web in unexpected ways. Structural properties such as food chain length, With the concern of focusing on this upstream role (does evolution design robust food webs?), we have developed a community evolution model describing the genesis of food webs. It shows that evolutionary history does not always shape food webs in a way that their functioning, at least for

(PDF) Nutrient enrichment and food chains: Can evolution buffer top ... Biology Diagrams
We show how evolutionary dynamics can alter the predictions of classical models of the effects of nutrient enrichment on food webs. We compare an ecological nutrient-plant-herbivore food-chain Food Chains are a crucial part of the food web and show how energy is passed along from one species to another, making it possible for all species to survive. Food Chains are also an important tool for studying the health and productivity of an ecosystem, helping to identify any potential issues with a species or with the environment. Objective: To conceptualize the agri-food chain and analyze its evolution during the 21st century: The taro case. Design/Methodology/Scope : A systematic literature review of magazines specialized in agri-food chains, value chains, logistics and supply chains for qualitative support and a case study of the taro agri-food chain were performed.
We focus on agri-food value chains to analyze their impact on food and The prevalence of overweight children follows the shape of a cubic function. Finally, dietary energy consumption shows a positive evolution over the period highlighting a potential evolution in food system transformation. Download: Download high-res image (223KB

