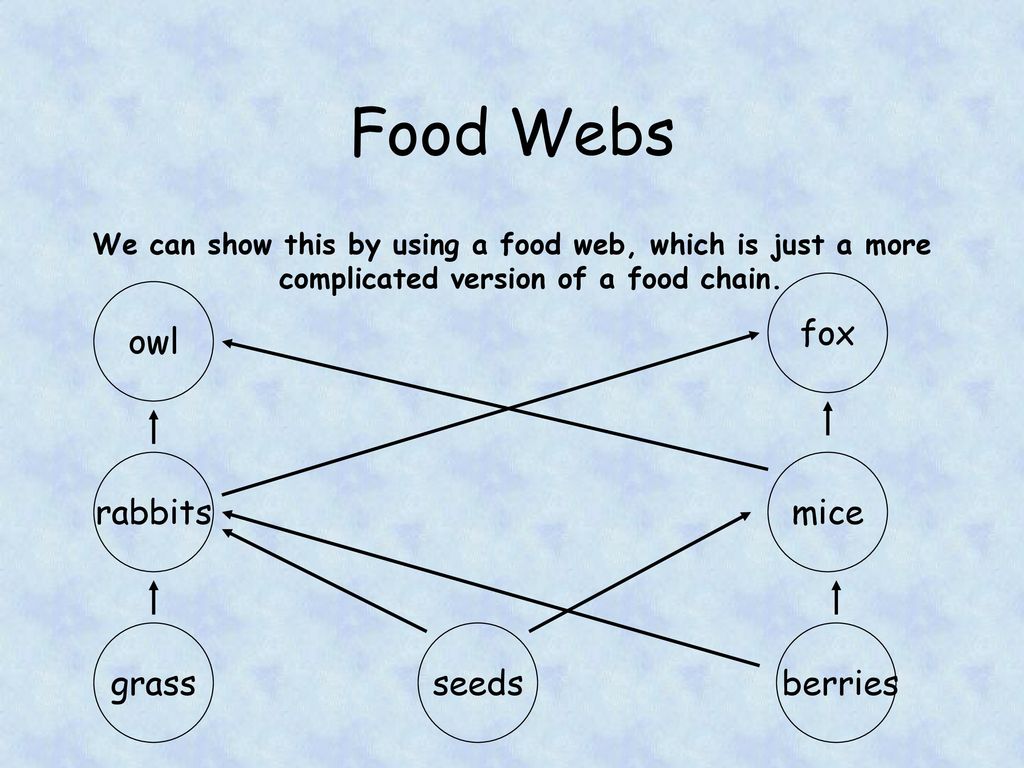
Grey Headed Flying Fox Biology Diagrams The 3rd level of a deciduous forest's food web includes the secondary consumers. These include foxes and owls (who eat the rodents) and birds, skunks and opposums, who eat insects. 4th Level This level are the predators, or tertiary consumers. One in a decidious forest is the cougar, which preys on deer and smaller animals. 1 Fox. 2 Stoat Polecat. 3 Feral cat. Mixed Forests: These ecosystems have a combination of different tree species. Deer, such as axis deer or fallow deer, can be found in mixed forests in various parts of the world. The primary food chain in a forest ecosystem includes producers such as plants, primary consumers such as herbivores The other food chain in the same ecosystem consists of the bird, the grasshopper, and the grass. Because the grass is also part of the food chain containing the rabbit and the fox, it makes up a food web within the same ecosystem. The size and the strength of the food chains within a food web depend upon what's known as biomass.

To understand the Deciduous Forest Food Web, Then read about the different trophic levels of a typical Food Chain (below). The trophic level is the position that an organism (plant or animal) occupies in a food chain - what it eats, and what eats it. Animals (fox, coyotes, eagles, owls) who eat the 1st & 2nd consumers are carnivores Organisms at different trophic levels in the deciduous forest depend on each other for survival. 1. Producers: Deciduous trees such as oaks, maples, and beeches are the predominant producers in this ecosystem.Small plants, flowers, ferns, and grasses are also abundant. 2. Primary Consumers: The second trophic level is inhabited by herbivorous animals such as deer, squirrels, rabbits What eats a fox in a food chain? The answer to this question lies in the hierarchy of a typical food chain or food web. Just like any other predator, foxes too have their natural enemies. Foxes are incredibly adaptable animals and can thrive in various environments, including forests, grasslands, mountains, and even urban areas. Their

Unraveling the Diet of the Cunning Fox in the Food Chain Biology Diagrams
The mixed habitat offers a variety of food and cover. (John Parker) CONTENTS Page Acknowledgements ii Summary iv 1. Aim and context 1 2. Fox ecology 2 Distribution 2 Social organisation, breeding and dispersal 3 has been due to an increase in forest area. Fox population densities range from less than 0.1 km in some upland areas to more

Examples in the deciduous forest food web are bears, hawks and large snakes like the anaconda. Decomposers. Decomposers like earthworms, bacteria, fungi and insects take care of the dead plants and animals in the deciduous forest. They break them down into smaller and smaller parts which ultimately creates new soil. The food web continues as