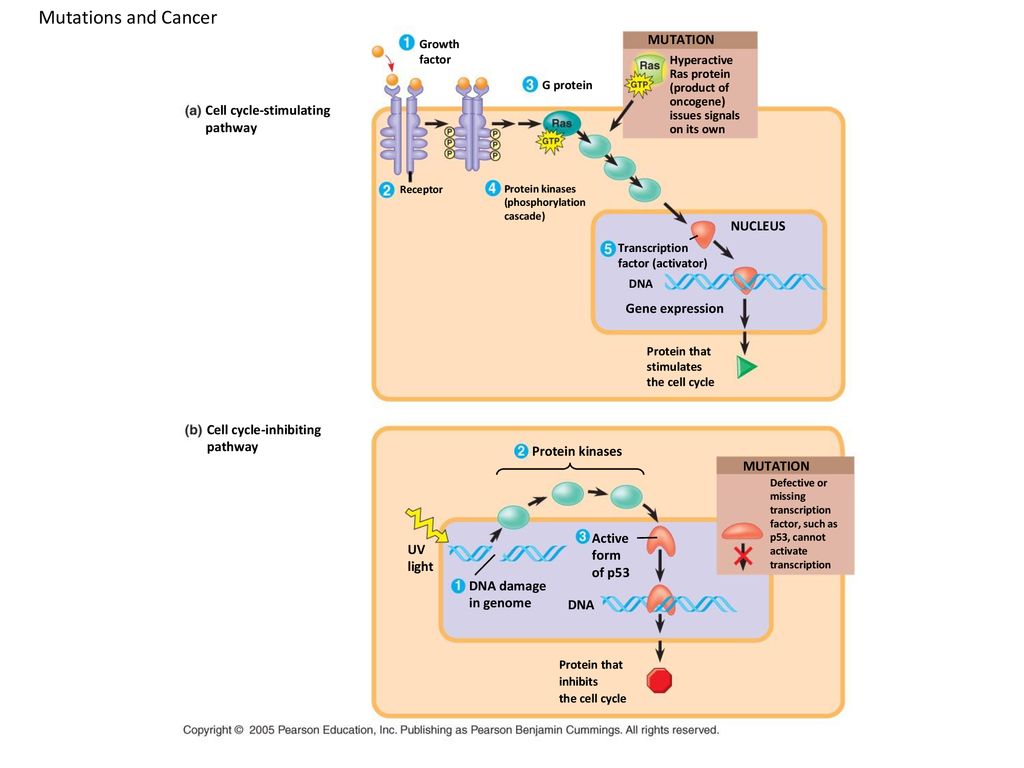
Overview of the mutation accumulation MA experiment A Ancestors Biology Diagrams The G1/S transition in mammalian cells. CycD is a sensor of mitogenic stimuli linking the cell cycle with the external environment. Growth factor‐induced cycD accumulation results in the formation of active cycD/cdk4, which overcomes inhibition by p16 and phosphorylates Rb. Cancer-associated mutations that perturb cell cycle control allow continuous cell division chiefly by compromising the ability of cells to exit the cell cycle. Cyclin D-CDK4/6 accumulation Cyclins and Kinases. The cell cycle is controlled by a number of protein-controlled feedback processes. Two types of proteins involved in the control of the cell cycle are kinases and cyclins.Cyclins activate kinases by binding to them, specifically they activate cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK).Kinases are enzymes that catalyze the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to another molecule in a

The cell cycle is a complex and strictly controlled process, consisting of different phases. Cell cycle regulation depends on phase-specific transcriptions of cell cycle genes. The alterations of cell cycle genes can predispose normal cells to have a cancerous phenotype. Indeed, several mechanisms underlying the deregulation of the cell cycle have been identified in different types of cancer Cell cycle checkpoints operate as DNA surveillance mechanisms that prevent the accumulation and propagation of genetic errors during cell division. Checkpoints can delay cell cycle progression or, in response to irreparable DNA damage, induce cell cycle exit or cell death. Cancer-associated mutations that perturb cell cycle control allow

Cell cycle checkpoints and their inactivation in human cancer Biology Diagrams
The cell cycle consists of the actual cell division stages (Mitosis) and the period between successive cell divisions, called the Interphase. Cancer results from an accumulation of somatic mutations in both TSGs and proto-oncogenes. Each new somatic mutation creates changes in the cell which contribute to the malignant phenotype. The rate at which DNA mutations accumulate varies substantially across cell types and tissues in the human body, but the origin of these differences is not well understood. This study develops a model to interpret "clock-like" mutation accumulation in humans, showing that the rate of accumulation depends on underlying processes of DNA damage, repair and replication.
Second, the aggregate of mutations within each cell affects the selection dynamics between clones. 108 Despite a life-long accumulation of mutations in stem cells, a lack of negative selection of deleterious mutations is evident in tissue homeostasis and cancer. 19, 109, 110 In somatic evolution, this phenomenon may be explained by the Explore how the cell cycle control system regulates cell division through key phases, proteins, and checkpoints to maintain genomic stability and prevent errors. TP53 mutations are found in over 50% of human cancers, often leading to an accumulation of additional mutations. Similarly, overactivation of CDK4 and CDK6, often due to CCND1

Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology Biology Diagrams
These complexes exert their regulatory function by phosphorylation of key proteins involved in cell cycle transitions, such as the product encoded by the retinoblastoma gene (pRB). Mutations and overexpression of cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases, mainly cyclin D1 and Cdk4, have been reported and proposed to be oncogenic events.

