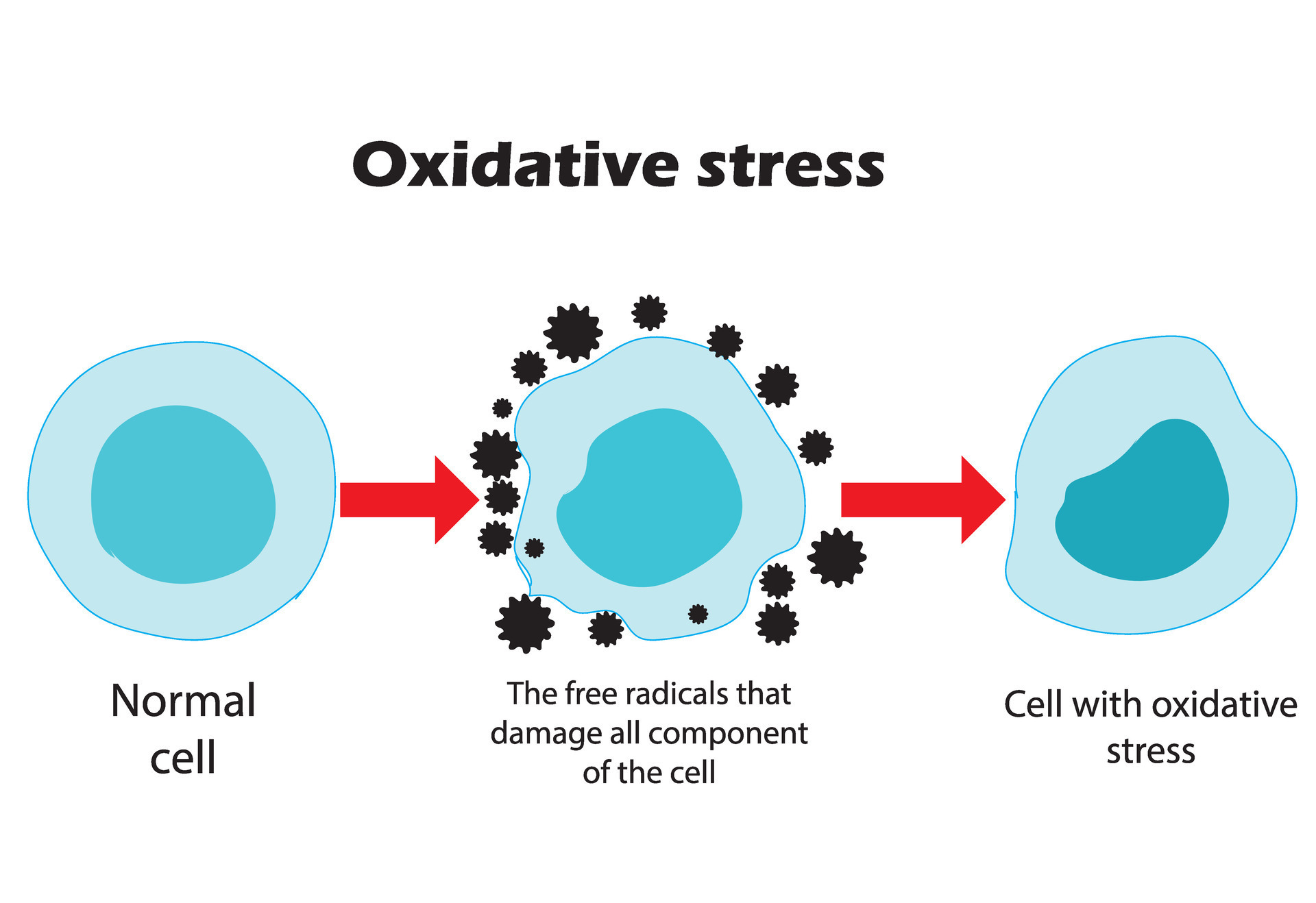
Oxidative stress From normal cells to oxidative stress and aggressive Biology Diagrams Oxidative stress is a phenomenon caused by an imbalance between production and accumulation of oxygen reactive species (ROS) in cells and tissues and the ability of a biological system to detoxify these reactive products. Prooxidant polyphenols seem to exert their cytotoxic activity by inducing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest via several The DNA damage response (DDR) is capable of repairing oxidative stress-induced DNA damage and the integrity of the genome is maintained. B) Cancer cells have an increased amount of ROS, shifting the redox balance of the cell. The increased oxidative stress inflicts damage on the DNA of the cancer cell, contributing to cancer's genomic instability.
Oxidative stress and cell death. There is a plethora of stimuli that can trigger the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), among them irradiation, toxins, and also normal metabolic processes. Cell Cycle. 2008;7(11):1511-1521. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.11.5959. [Google Scholar] 36. Eskelinen E-L. New insights into the mechanisms of

Oxidative stress and cell cycle checkpoint function Biology Diagrams
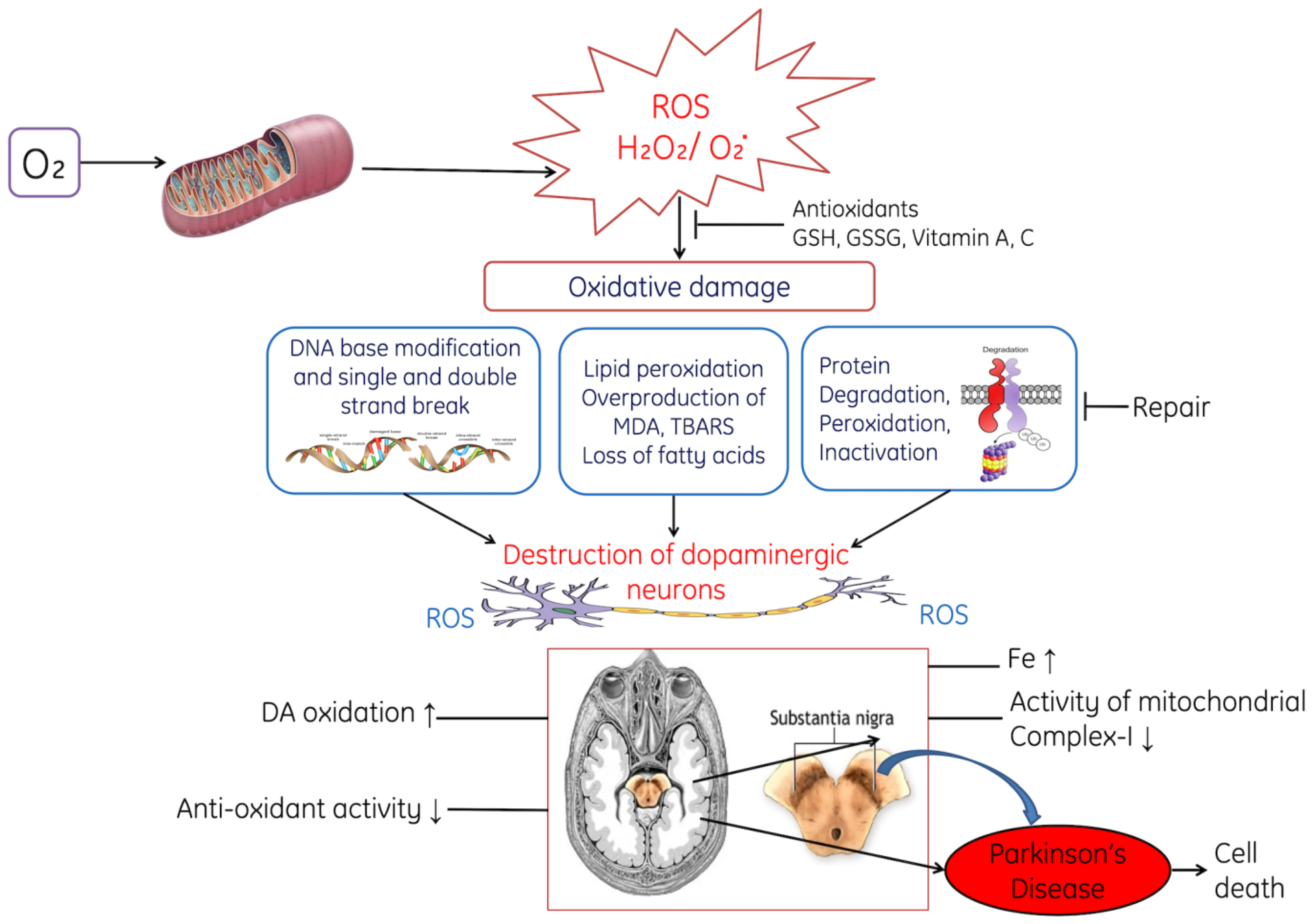
Oxidative stress was first demonstrated to damage living organisms in 1952, when Conger and Fairchild [14] demonstrated that increases in oxygen pressure could cause chromosomal aberrations in pollen grains. Since this time oxygen and ROS have been found to induce many types of DNA damage, including single- and double-stranded DNA breaks, base and sugar modifications, DNA-protein crosslinks Oxidative stress and cell cycle reentry lead to cell death in the harlequin mouse. An 80% reduction of AIF protein expression in the Hq mutant mouse is associated with increased activity of total glutathione (GSH) and catalase, presumably through increases in hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2).Surviving neurons may express additional antioxidant pathways.
ROS, oxidative stress, and the redox state in general, may play an important role in controlling certain stages of the cell cycle. Indeed, the concept that redox state, ROS production, and progression into mitosis might be intertwined is an old one (Kawamura, 1960; Mazia, 1958), but the connection remains poorly understood, paradoxical, and sometimes conflicting.

ROS and Oxidative Stress Are Elevated in Mitosis during ... Biology Diagrams
In response to oxidative stress, cells typically undergo cell cycle arrest and enter the G 0 phase (i.e., a quiescent, non-dividing stage) due to activation of the p53-regulated cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21, which halts cell cycle progression and inhibits DNA synthesis [23,24].

