Ribosomal control in RNA virusinfected cells Biology Diagrams Messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules carry the coding sequences for protein synthesis and are called transcripts; ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules form the core of a cell's ribosomes (the structures in Composed of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins, these structures are found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, with some differences in size and composition. In eukaryotes, ribosomes can be found either floating freely in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum, forming the rough ER.
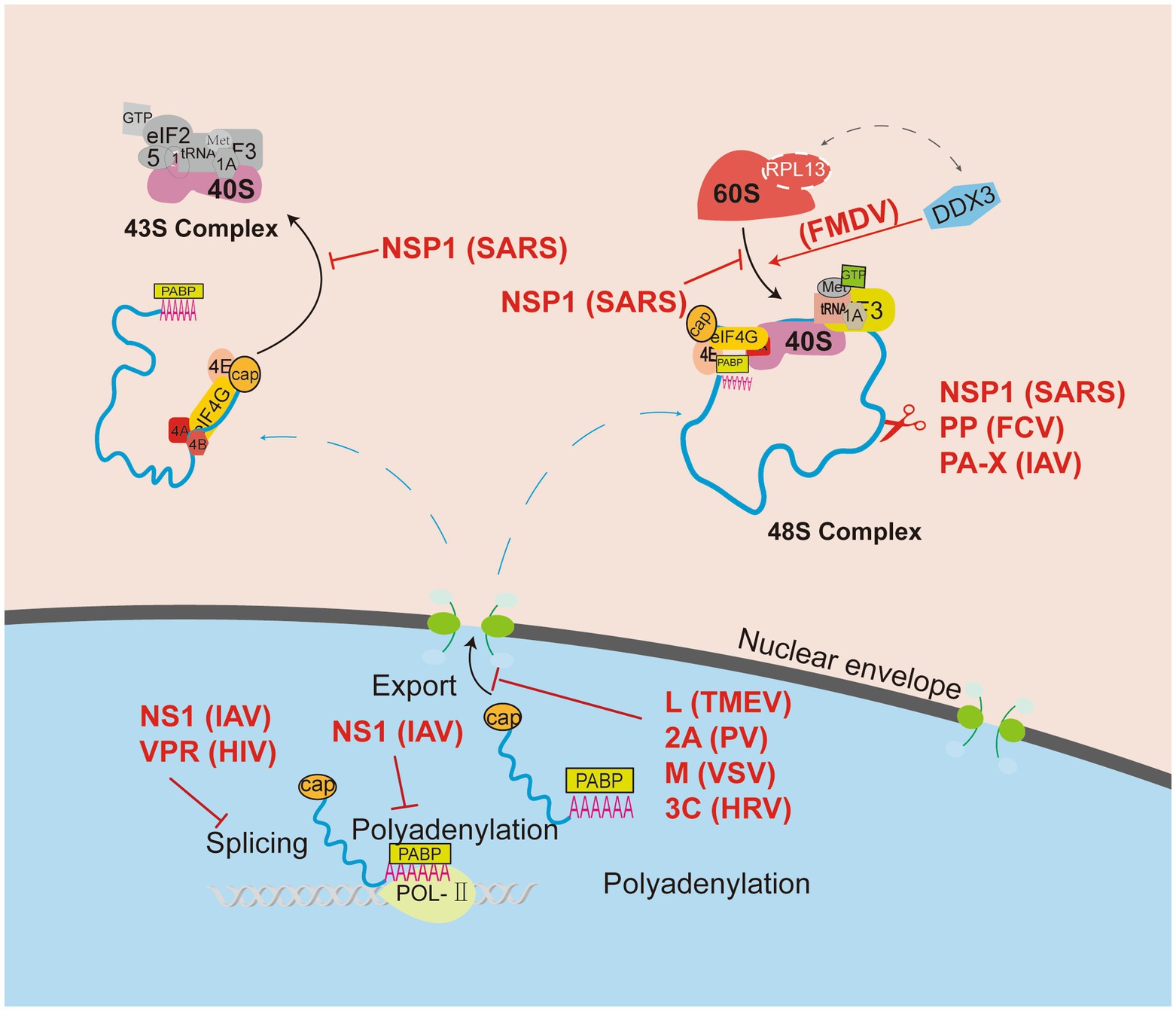
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a key component of the cellular machinery responsible for protein synthesis, playing a role in translating genetic information into proteins. Its importance lies in its structural presence within ribosomes and its active participation in various phases of translation.

rRNA's Role in Protein Synthesis and Translation Processes Biology Diagrams
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) - subunits of ribosomes. Transfer RNA (tRNA) - carries amino acids to the ribosomes. Central Dogma - DNA codes for RNA, which codes for protein. Transcription (DNA --> RNA) Base pair rule ( Guanine to Cytosine; Adenine to Uracil) One side of the DNA is the template. RNA polymerase builds a strand of RNA based on the

Ribosomes are biological machines that consist of RNA and proteins. Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis, translating genetic information into functional proteins. They consist of two subunits made of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins. Ribosomes occur in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, differing slightly in size and composition.

Ribosomes Function, Structure, and Facts Biology Diagrams
Ribosomal RNA is a molecule in cells that forms part of the protein-synthesizing organelle known as a ribosome and that is exported to the cytoplasm to help translate the information in messenger Protein synthesis Ribosomes are key components of protein synthesis in cells. (more) ribosomal RNA. genetics. Ask the Chatbot a Question More Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is the RNA component of ribosomes, the molecular machines that catalyze protein synthesis. Ribosomal RNA constitute over sixty percent of the ribosome by weight and are crucial for all its functions - from binding to mRNA and recruiting tRNA to catalyzing the formation of a peptide bond between two amino acids. Protein synthesis is accomplished by orderly interactions between mRNA and the other ribonucleic acids (transfer RNA [tRNA] and ribosomal RNA [rRNA]), the ribosome, and more than 100 enzymes. The mRNA formed in the nucleus during transcription is transported across the nuclear membrane into the cytoplasm to the ribosomes—carrying with it the

